Calculate Date Differences in Google Sheets between two dates is a common task in spreadsheets, whether you’re managing a project timeline, tracking an employee’s tenure, or calculating a customer’s subscription duration. Google Sheets provides the DATEDIF function, a powerful yet often underused tool, to perform these calculations seamlessly. Calculate Date Differences in Google Sheets
In this tutorial, you’ll learn how to use the DATEDIF function in Google Sheets, along with practical examples and tips to maximize its potential.
Why Use the Calculate Date Differences in Google Sheets DATEDIF Function?
The DATEDIF function is specifically designed to calculate date differences in various units, such as days, months, or years. It offers a simple way to determine:
- The number of days between two dates.
- The months or years elapsed.
- A combination of days, months, and years.
This function can simplify your workflow and improve the accuracy of your calculations.
The Syntax of DATEDIF
Before diving into examples, let’s explore the syntax of the DATEDIF function:
=DATEDIF(start_date, end_date, unit)
- start_date: The earlier date in the range (required).
- end_date: The later date in the range (required).
- unit: Specifies the type of difference to calculate (required).
Supported Units
- “Y”: Total number of complete years.
- “M”: Total number of complete months.
- “D”: Total number of days.
- “MD”: Difference in days, ignoring months and years.
- “YM”: Difference in months, ignoring years.
- “YD”: Difference in days, ignoring years.
How to Use DATEDIF in Google Sheets
-
Calculate Total Number of Days
If you want to calculate the total days between two dates:
- Formula Example:
=DATEDIF(A2, B2, “D”)
Input:
- A2: Start date (e.g., 01/01/2023)
- B2: End date (e.g., 12/31/2023)
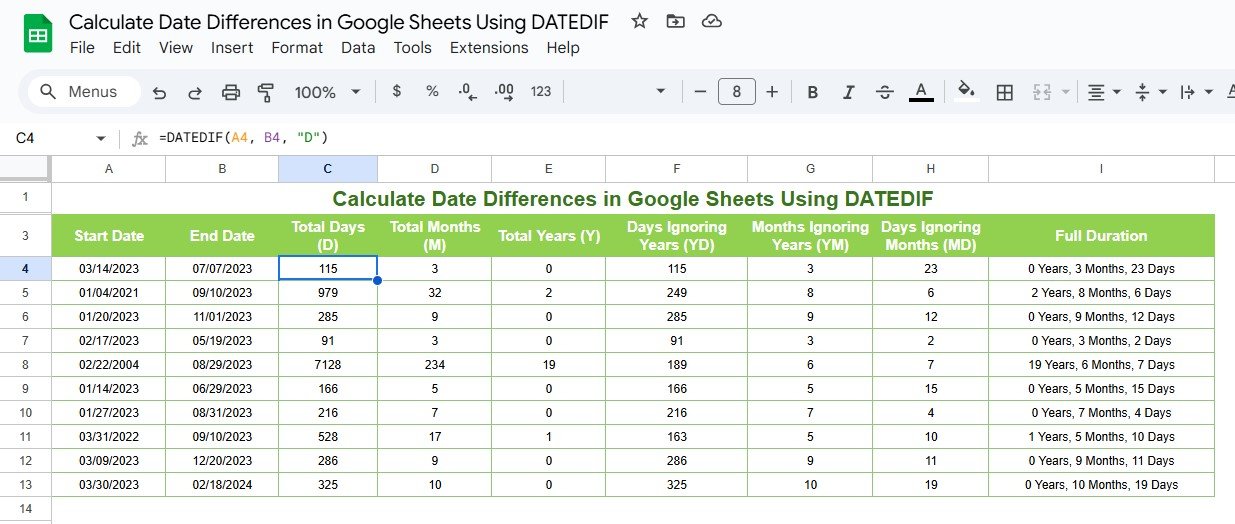
Output:
- The number of days between the two dates (365 days).
Use Case:
This is particularly helpful for calculating deadlines or durations in project management.
-
Calculate Total Number of Months
To find the complete months between two dates:
- Formula Example:
=DATEDIF(A2, B2, “M”)
Input:
- A2: Start date (e.g., 01/01/2023)
- B2: End date (e.g., 12/31/2023)
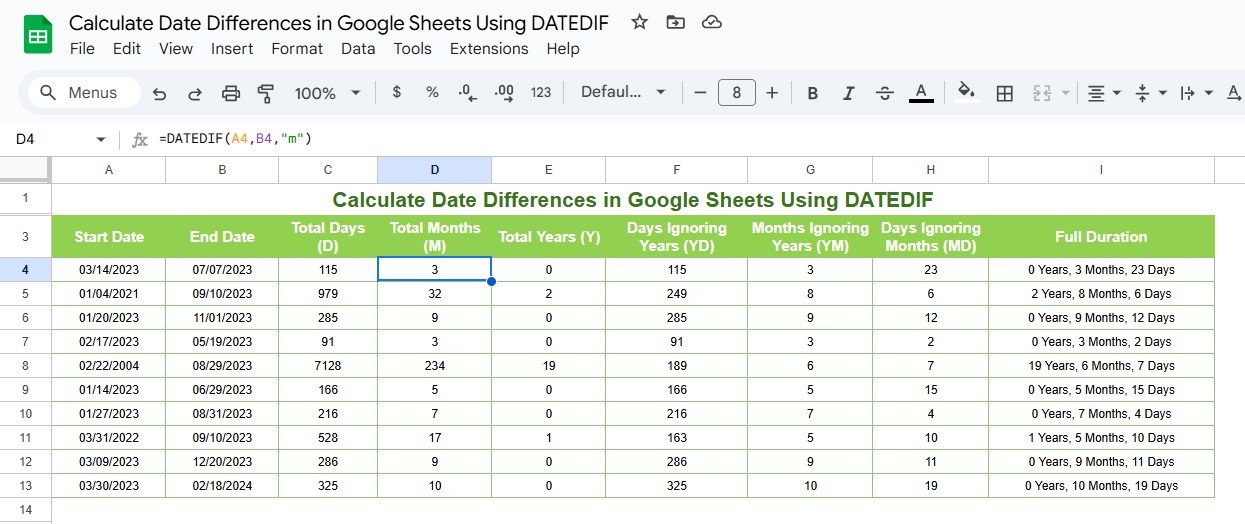
Output:
- The number of complete months (11 months).
Use Case:
Use this formula to track subscription periods or billing cycles.
-
Calculate Total Number of Years
For calculating the complete years between two dates:
- Formula Example:
=DATEDIF(A2, B2, “Y”)
Input:
- A2: Start date (e.g., 01/01/2020)
- B2: End date (e.g., 01/01/2024)
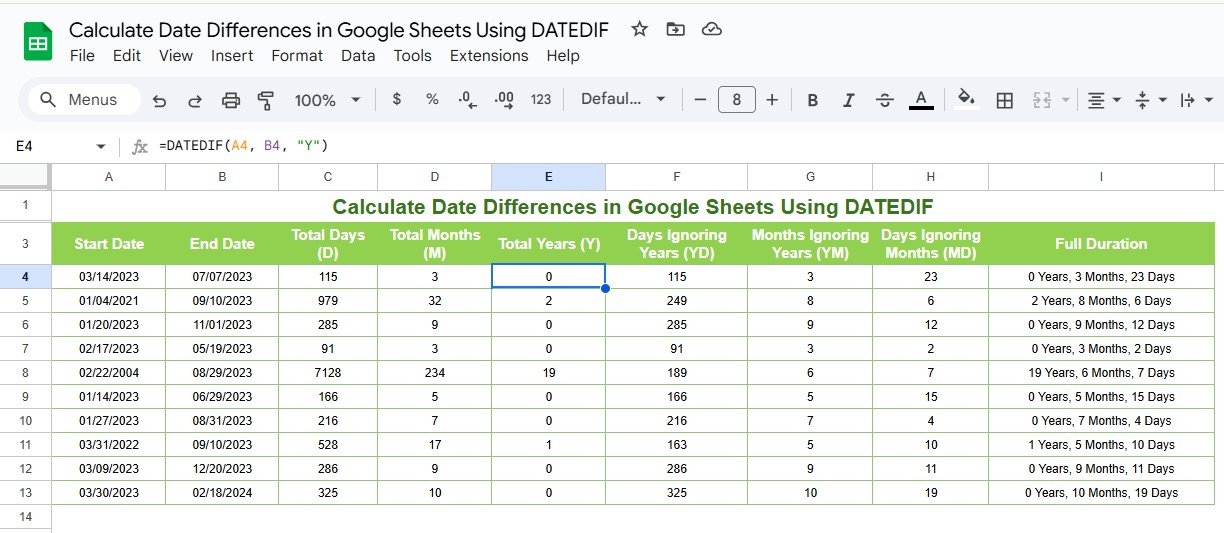
Output:
- The total years elapsed (4 years).
Use Case:
This is ideal for calculating service anniversaries or retirement eligibility.
-
Calculate Days Ignoring Years (“YD”)
To find the difference in days while ignoring the year component:
- Formula Example:
=DATEDIF(A2, B2, “YD”)
Input:
- A2: Start date (e.g., 12/25/2023)
- B2: End date (e.g., 01/01/2024)
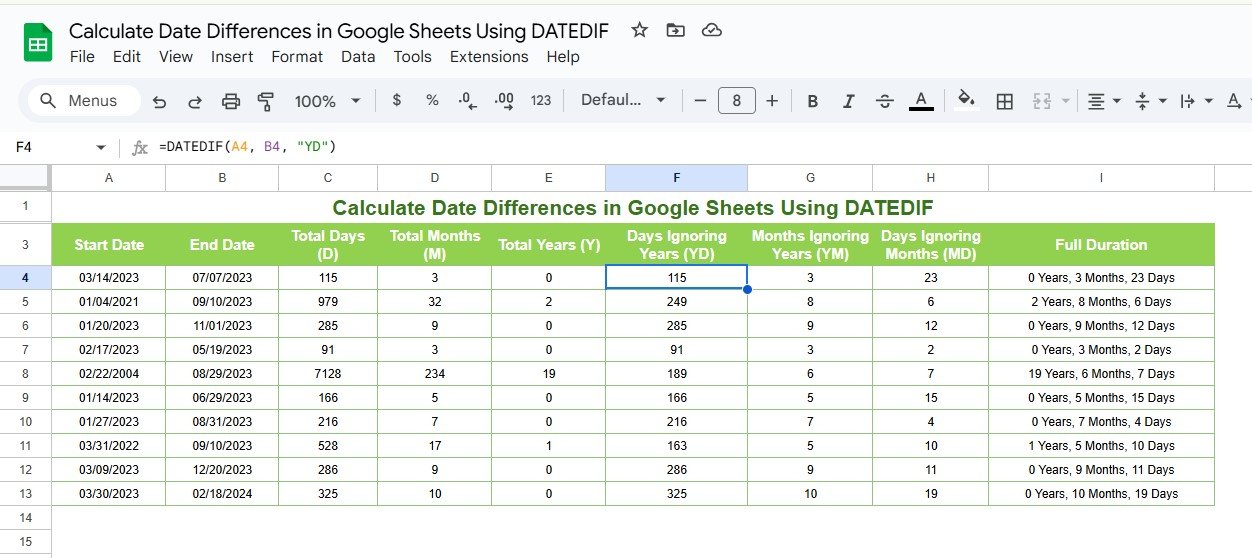
Output:
- The difference in days (7 days).
Use Case:
This is useful for recurring annual events, like birthdays or holidays.
-
Calculate Months Ignoring Years (“YM”)
If you want to find the number of months between two dates but ignore the years:
- Formula Example:
=DATEDIF(A2, B2, “YM”)
Input:
- A2: Start date (e.g., 01/15/2022)
- B2: End date (e.g., 03/15/2023)
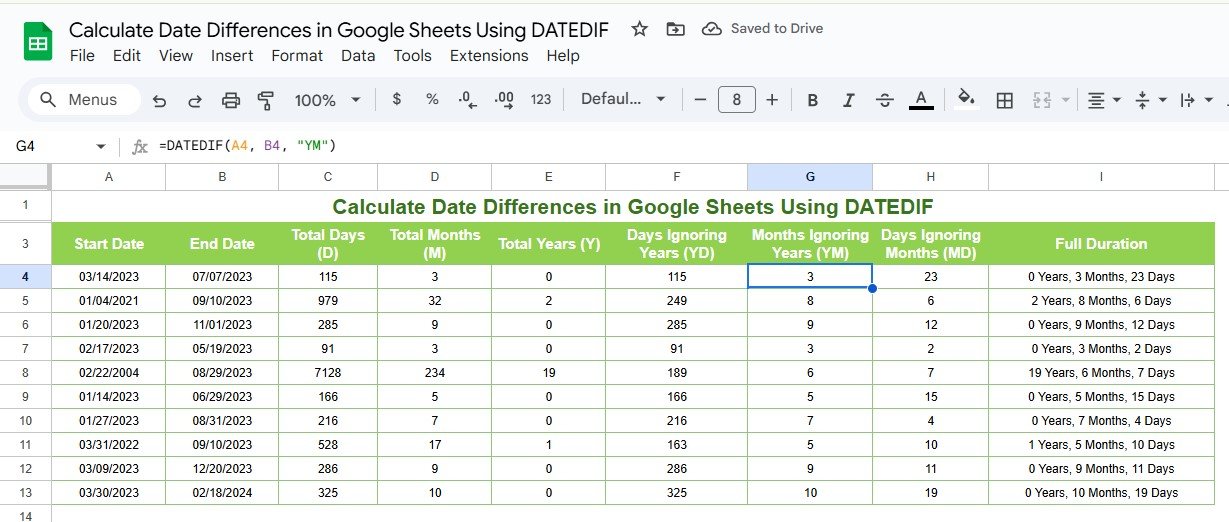
Output:
- The difference in months (2 months).
Use Case:
Ideal for comparing contract periods that start and end in different years.
-
Calculate Days Ignoring Months (“MD”)
To find the days left after subtracting full months and years:
- Formula Example:
=DATEDIF(A2, B2, “MD”)
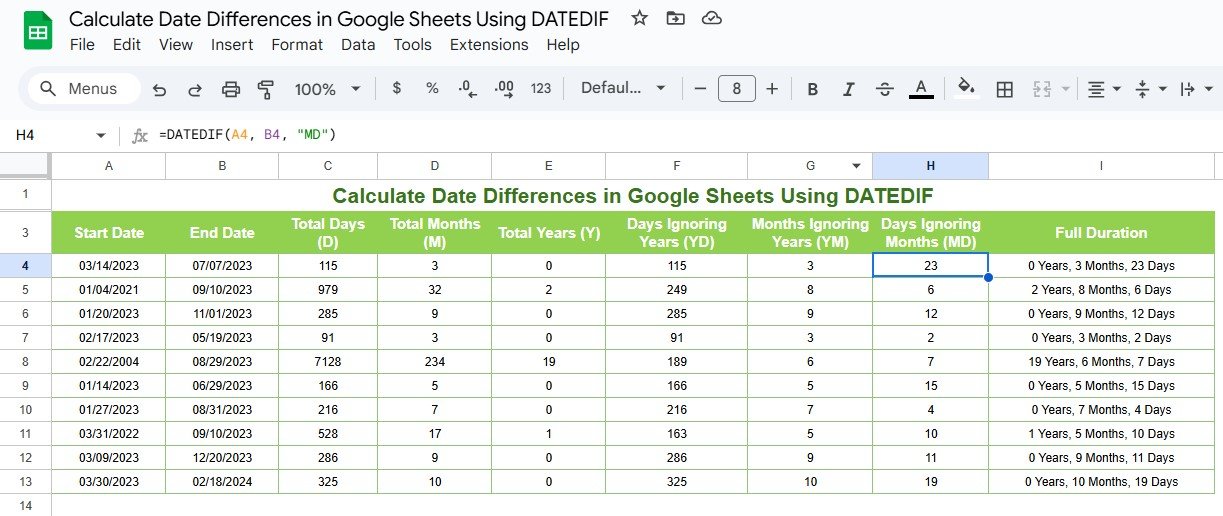
Input:
- A2: Start date (e.g., 01/30/2023)
- B2: End date (e.g., 02/10/2023)
Output:
- The difference in days (10 days).
Use Case:
Perfect for calculating the remaining days in a specific billing cycle.
Combining DATEDIF with Other Formulas
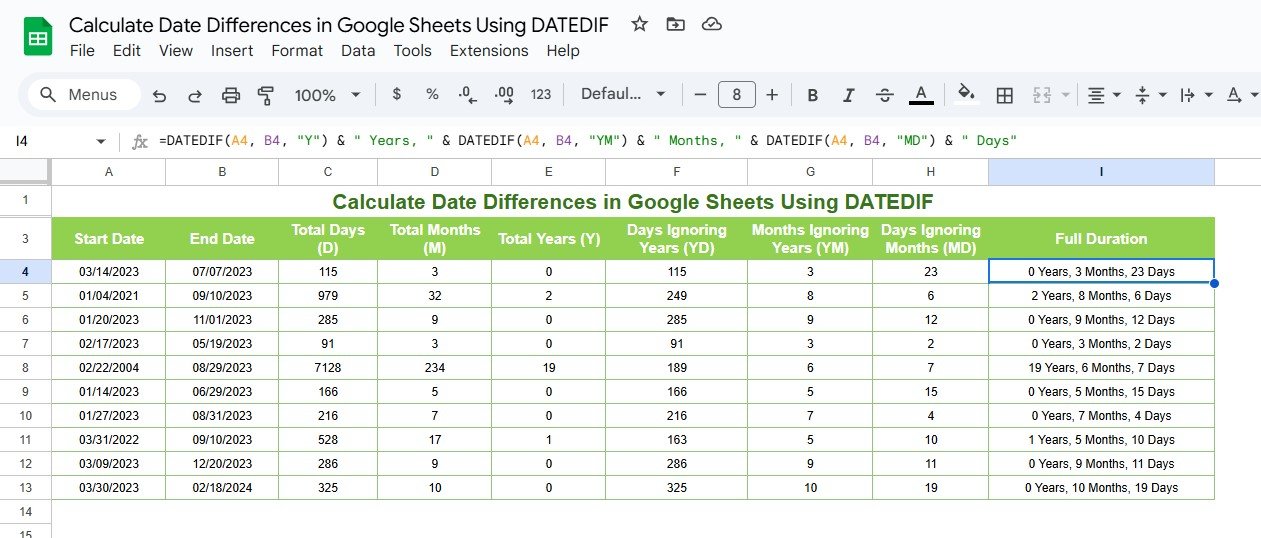
Example 1: Create a Full Duration Breakdown
To display a complete breakdown of years, months, and days:
Formula:
=DATEDIF(A2, B2, “Y”) & ” Years, ” & DATEDIF(A2, B2, “YM”) & ” Months, ” & DATEDIF(A2, B2, “MD”) & ” Days”
Output:
- 2 Years, 3 Months, 10 Days
Example 2: Conditional Formatting Based on Date Differences
Highlight cells where the date difference exceeds a certain threshold:
Steps:
- Use the formula =DATEDIF(A2, B2, “D”) > 30 in the conditional formatting rule.
- Apply a custom color to highlight rows exceeding 30 days.
Tips for Using DATEDIF Effectively
- Ensure Valid Dates:
Double-check that your date columns are formatted correctly. Invalid dates may result in errors. - Handle Errors Gracefully:
Wrap the DATEDIF function with IFERROR to avoid issues:
- Combine with TODAY Function:
Use the TODAY() function to calculate durations relative to the current date
Real-World Applications
- Project Management: Calculate project deadlines and overdue tasks.
- HR and Payroll: Determine employee tenure for benefits or pay raises.
- Subscription Tracking: Track the validity of service subscriptions or trial periods.
- Event Planning: Calculate countdowns to special events or holidays.
Conclusion
The DATEDIF function in Google Sheets is an incredibly versatile tool for calculating date differences. Whether you need to determine days, months, or years between dates, this function makes the process quick and easy. By combining it with other formulas and formatting options, you can unlock even more power for your spreadsheets. Calculate Date Differences in Google Sheets
Visit our YouTube channel to learn step-by-step video tutorials
Youtube.com/@NeotechNavigators